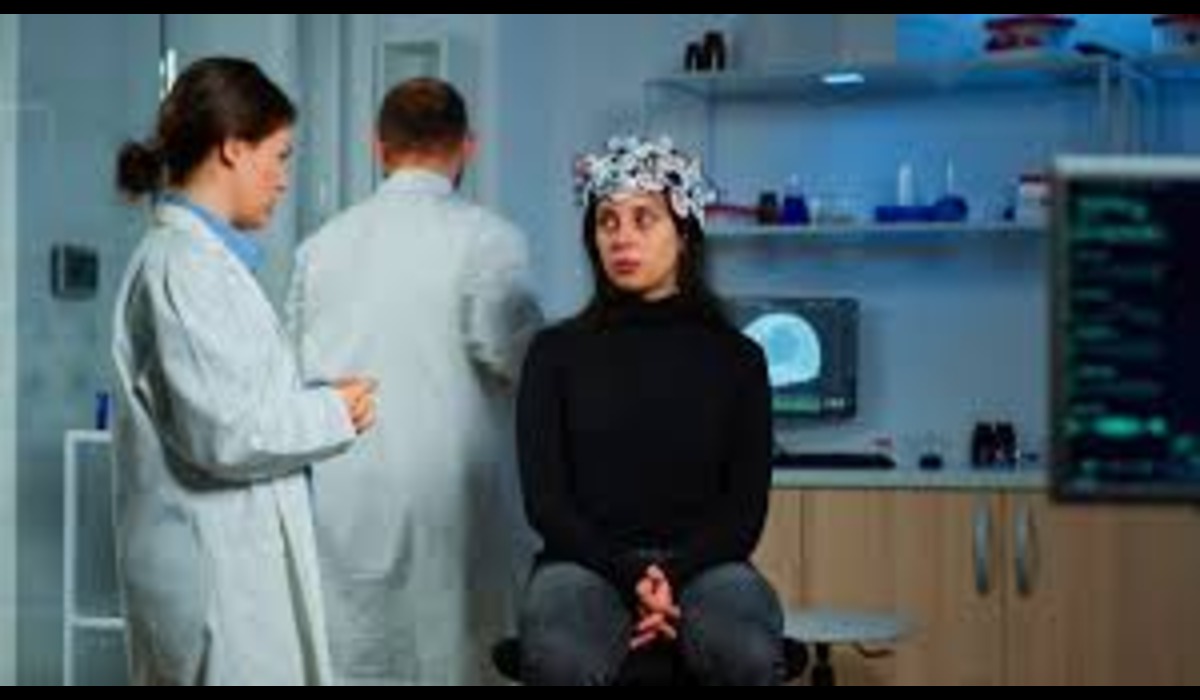
In recent years, the term “fearscans” has gained attention in various fields, including technology, psychology, and personal safety. This article will cover what fearscans are, how they work, their applications, and their potential advantages and disadvantages. We will also answer common questions about fearscanss to provide a comprehensive understanding of this new technology.
What are fearscans?
fearscans are a type of advanced scanning technology designed to detect and analyze emotional states, particularly anxiety. These scans use a combination of biometric sensors, algorithms, and data analytics to evaluate how a person responds to certain stimuli or situations. The technology can measure physiological responses such as heart rate, skin conductance, and facial expressions to determine a person’s level of anxiety.
How do anxiety scanners work?
fearscans work in a multi-step process. First, the technology collects data from various biometric sensors attached to the person’s body or integrated into their environment. These sensors monitor physiological indicators such as changes in heart rate, sweat production, and muscle tension.
Once the data is collected, it is analyzed using sophisticated algorithms designed to interpret emotional responses. The algorithms assess the intensity and type of fear response, often comparing it to a baseline measurement to identify any significant deviations.
The analysis results are presented in a format that can be easily interpreted by researchers, security personnel, or medical professionals. This may include graphical representations, statistical data, or descriptive reports describing the individual’s fear level and any relevant patterns.
Fearscans Apps
Fear scans have a wide range of potential applications. In the security field, they can be used to assess the emotional state of people in high-risk situations. This can be particularly useful in areas such as airport security or border control, where detecting signs of anxiety or fear can help identify potential threats.
In psychology and mental health, fear scans can be used to study anxiety disorders and phobias. By analyzing how people respond to anxiety-provoking stimuli, researchers can gain insight into the mechanisms underlying these disorders and develop more effective treatments.
Additionally, scare scanners have potential applications in entertainment and virtual reality. By understanding how users respond to fear in immersive environments, developers can create more engaging and realistic experiences that adapt to different levels of comfort and excitement.
Benefits of fearscans
One of the main benefits of anxiety scanners is their ability to provide objective data about emotional responses. Traditional methods of anxiety assessment, such as surveys or self-reported interviews, can be subjective and influenced by various factors. Anxiety scans offer a more quantifiable approach and allow for a clearer understanding of a person’s emotional state.
Another benefit is the ability to detect emotional distress early on. By monitoring physiological responses, anxiety scanners can detect signs of anxiety or fear before they become more pronounced. This can be particularly useful in situations where early intervention can make a significant difference, such as mental health treatment or security screening.
Disadvantages and Concerns
Despite their benefits, fearscansalso raise concerns. Privacy is a major issue, as the technology involves the collection of sensitive biometric data. There is a risk that this data could be misused or accessed without appropriate consent, potentially leading to privacy violations.
Another concern is the accuracy of fearscans While the technology is advanced, it is not perfect. Factors such as individual differences in physiological responses or the presence of external stressors can affect the accuracy of scans, meaning that results should be interpreted with caution and in conjunction with other information.
There is also the potential for over-reliance on fear exploration in decision-making processes. For example, in security settings, an anxiety scan may indicate heightened anxiety, but this does not necessarily mean that a person poses a threat. Relying solely on anxiety scan data
could lead to false positives and potentially unfair treatment.
Conclusion
fearscans represent an exciting technological advancement that has the potential to impact a variety of areas, from security to mental health. While they provide valuable insight into emotional responses, it is important to consider their limitations and address privacy concerns. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications and impacts are likely to grow, offering new opportunities and challenges for understanding and managing anxiety.